Shifts of the market supply curve occur when the quantity of goods producers are willing to supply changes due to factors other than the price of the good itself. These factors can include technological advancements, changes in production costs, government regulations, and external events such as natural disasters or political instability. Understanding these shifts is crucial for businesses, economists, and policymakers as they affect market prices, production levels, and economic stability.
For businesses, recognizing shifts in the supply curve helps in adjusting production plans, managing inventory, and setting competitive prices. Economists analyze these shifts to predict market behavior, assess economic trends, and provide insights into overall economic health. Policymakers use this information to design effective policies that promote economic growth, stability, and sustainability.
By comprehending the underlying causes of supply curve shifts, stakeholders can make informed decisions that optimize production efficiency, allocate resources wisely, and maintain a balance between supply and demand. This understanding contributes to a more resilient and adaptable economic system, capable of responding to changing conditions and ensuring long-term stability.
1. What Are Shifts of the Market Supply Curve?
A shift of the supply curve means that at every price level, the quantity supplied changes due to external factors like production costs, technology, or government policies. This differs from movement along the supply curve, which is caused by price changes.
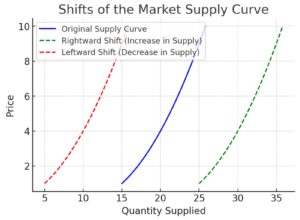
A. Key Features of Supply Curve Shifts
- Entire Curve Movement: The supply curve shifts left or right.
- Non-Price Factors: Changes are driven by factors other than price.
- Market Impact: Alters the equilibrium price and quantity in the market.
2. Types of Supply Curve Shifts
A. Rightward Shift (Increase in Supply)
- Definition: More quantity supplied at every price level.
- Causes: Improved technology, lower input costs, government subsidies, and favorable market conditions.
B. Leftward Shift (Decrease in Supply)
- Definition: Less quantity supplied at every price level.
- Causes: Higher input costs, new taxes, supply chain disruptions, and adverse natural conditions.
3. Causes of Supply Curve Shifts
A. Changes in Production Costs
- Cause: Lower costs increase supply; higher costs decrease supply.
B. Technological Advancements
- Cause: New technology enhances efficiency, increasing supply.
C. Government Policies
- Cause: Subsidies increase supply; taxes and regulations reduce supply.
D. Prices of Related Goods
- Cause: Higher prices of substitute goods may decrease supply of the current good.
E. Market Competition
- Cause: More suppliers increase supply; fewer suppliers decrease supply.
F. Natural Factors
- Cause: Weather, natural disasters, and resource availability affect supply.
G. Future Expectations
- Cause: Expectations of higher future prices may reduce current supply.
4. Impact of Supply Curve Shifts on the Market
A. Price Changes
- Impact: Increased supply lowers prices, while decreased supply raises prices.
B. Production Adjustments
- Impact: Producers adjust output levels based on supply shifts.
C. Consumer Behavior
- Impact: Changes in supply influence consumer purchasing patterns.
D. Business Strategies
- Impact: Companies revise pricing, inventory, and marketing strategies.
5. Elasticity of Supply and Curve Shifts
A. Price Elasticity of Supply
- Concept: Measures responsiveness of supply to price changes.
B. Impact on Shifts
- Role: More elastic supply responds faster to external changes.
6. Examples of Supply Curve Shifts
A. Agricultural Products
- Example: Favorable weather increases supply, shifting the curve rightward.
B. Technology Industry
- Example: New manufacturing technology increases supply of electronics.
C. Oil Market
- Example: Political instability reduces supply, shifting the curve leftward.
7. Challenges in Analyzing Supply Curve Shifts
A. Data Accuracy
- Challenge: Obtaining reliable supply data is complex.
B. Market Volatility
- Challenge: Rapid market changes complicate supply analysis.
C. External Shocks
- Challenge: Unforeseen events like pandemics disrupt supply.
8. The Significance of Supply Curve Shifts in Economics
Shifts in the market supply curve have profound effects on prices, production, and market stability. These shifts occur due to factors such as changes in production costs, technological advancements, government regulations, and external events like natural disasters or political instability. By understanding and analyzing these shifts, businesses can optimize their operations, make informed production decisions, and manage inventory effectively.
For policymakers, insights into supply curve shifts are essential for designing effective interventions that promote economic stability and growth. By anticipating how supply changes will impact the market, policymakers can implement strategies to address potential shortages or surpluses, regulate prices, and ensure a steady supply of goods and services to meet consumer demand. This knowledge is crucial for maintaining economic stability and avoiding market disruptions.
Economists rely on the analysis of supply curve shifts to gain a deeper understanding of market behavior and predict future trends. By studying these shifts, economists can provide valuable insights into the overall health of the economy, identify potential challenges, and recommend measures to enhance economic resilience. Understanding the dynamics of supply curve shifts also helps in forecasting economic performance and guiding long-term planning.
In summary, the significance of supply curve shifts in economics cannot be overstated. They play a critical role in shaping market dynamics, influencing prices, and determining production levels. By analyzing these shifts, businesses, policymakers, and economists can make informed decisions that optimize market functioning, ensure efficient resource allocation, and contribute to sustainable economic growth. This comprehensive understanding of supply curve shifts is essential for achieving a balanced and thriving economy.